WHAT IS CAST METALS ENGINEERING?
- IT PRODUCES PRECISION ENGINEERED COMPONENTS
- IT IS SHAPING THE WORLD THAT WE LIVE IN
- IT INVOLVES MAKING THINGS WITH RECYCLED METAL, HELPING THE PLANET
Cast components are used in all areas of everyday life – in cars, trains and planes, from renewable energy generation to mobile phones – our industry takes metal and recycles it into new engineered parts.
Put simply, casting is liquid metal engineering!
However, there’s so much more to it than that, with all types of engineers from designers, machinists, technicians, analysts and so many more required to then turn cast metal into end products.
But let’s start with casting and go from there…
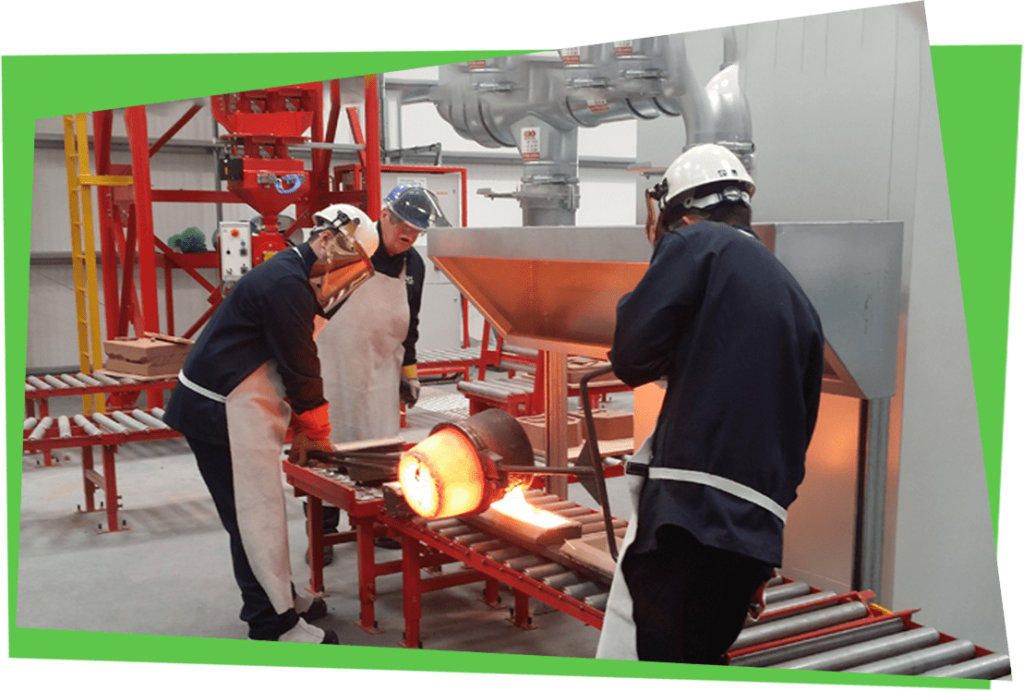

What does casting involve?
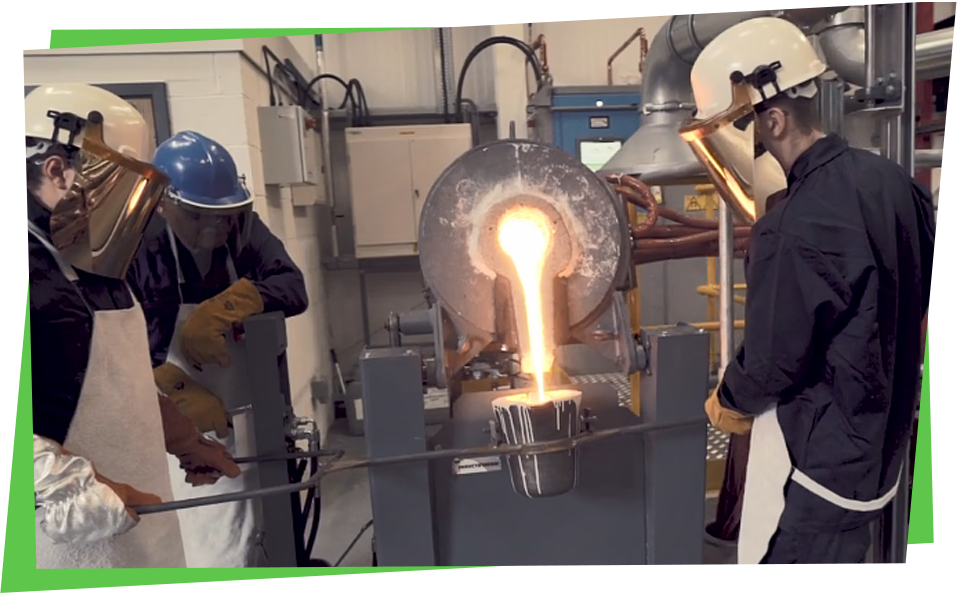

Casting happens in engineering companies known as foundries. Castings are made by pouring molten metal into a mould. Castings can be used to make parts or complex shapes that would be difficult or uneconomic to make by other methods (such as forging, assembling components or cutting from solid material).
Why is casting important?
The castings industry is growing, and more than 100 million tonnes of castings were produced globally last year, more than ever before!
It is also part of the ‘circular economy’, because most castings are made from recycled metal which have been thrown away. This reduces a huge amount of waste every year and metal recycles forever.

A green industry
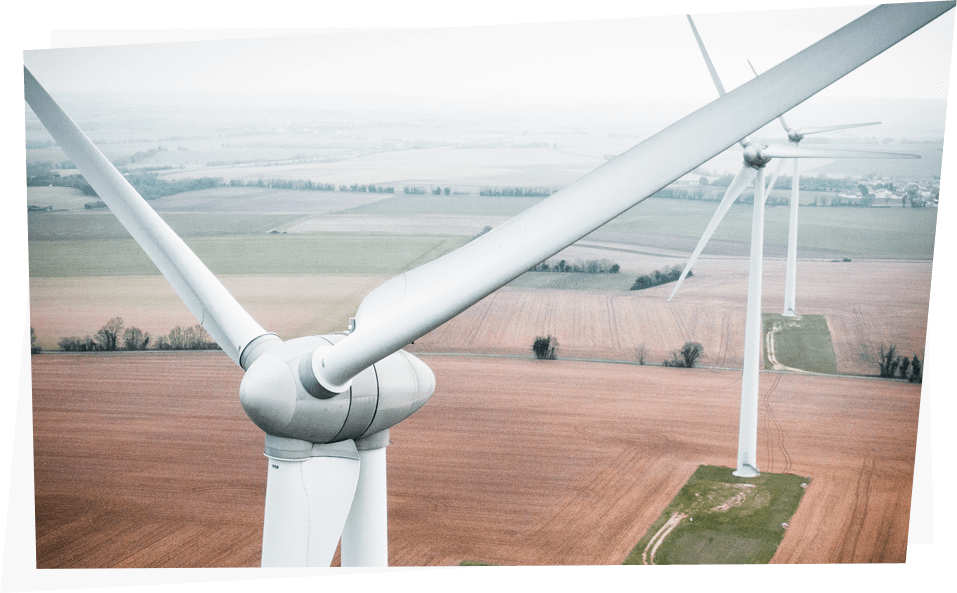

- Most castings are made from recycled metal so without castings there would be piles of scrap metal damaging our local environment.
- Castings are used in wind turbines and tidal power installations so we help the global environment.
- Foundries recycle most of the sand they use, repeatedly!
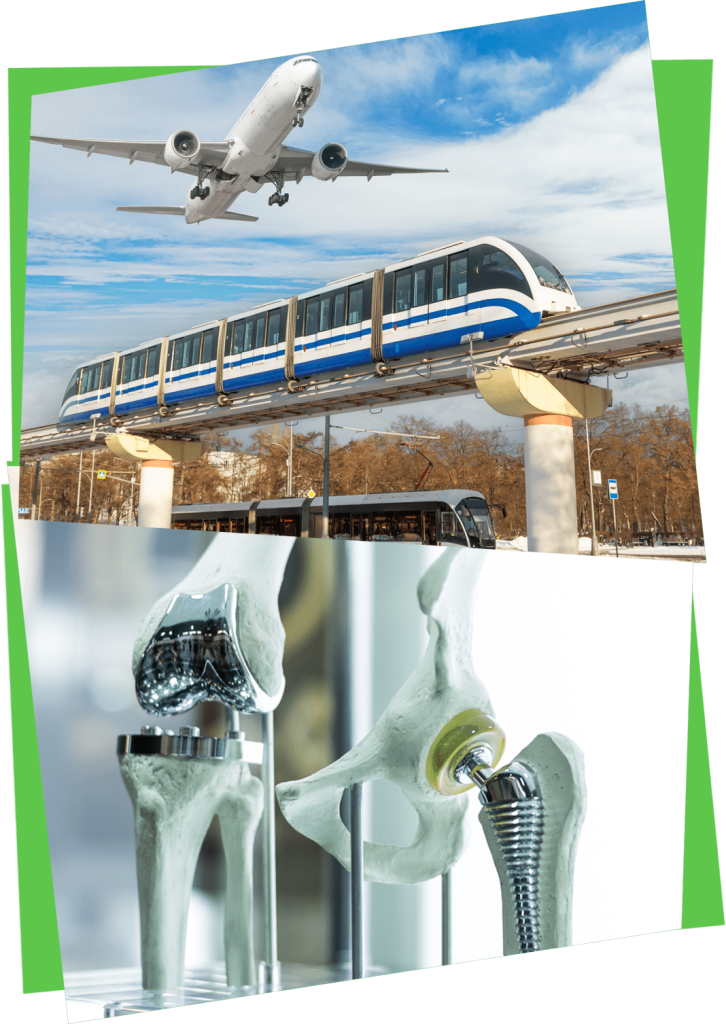
What do we make?
Here are a few examples of castings in the world around us:
- For the car industry: engine blocks, cylinder heads and cylinders, brake discs, wheels, brake callipers, turbo charger wheels and housings.
- For the water industry: pipes, taps, pumps and valves.
- For the energy industry: motors, generators, industrial gas turbines and wind energy hubs.
- For the rail industry: track crossings, brakes and wheels.
- For the aerospace industry: turbine blades, runway lighting and aircraft seats
- For the medical industry: hip and knee implants, medical scanners and wheelchair components.
- For the urban environment: street furniture, locks, lamp stands, sculptures and bike frames.

Did you know?
- All of the turbine blades in modern jet engines are castings!
- Foundries in the UK cast all of the engines for Formula One!
- A hybrid car typically includes over 100 castings.
- Wind energy and tidal energy installations both rely on castings to make the parts they need.
- Simulation, additive manufacturing and CAD design are important tools used by foundries.




